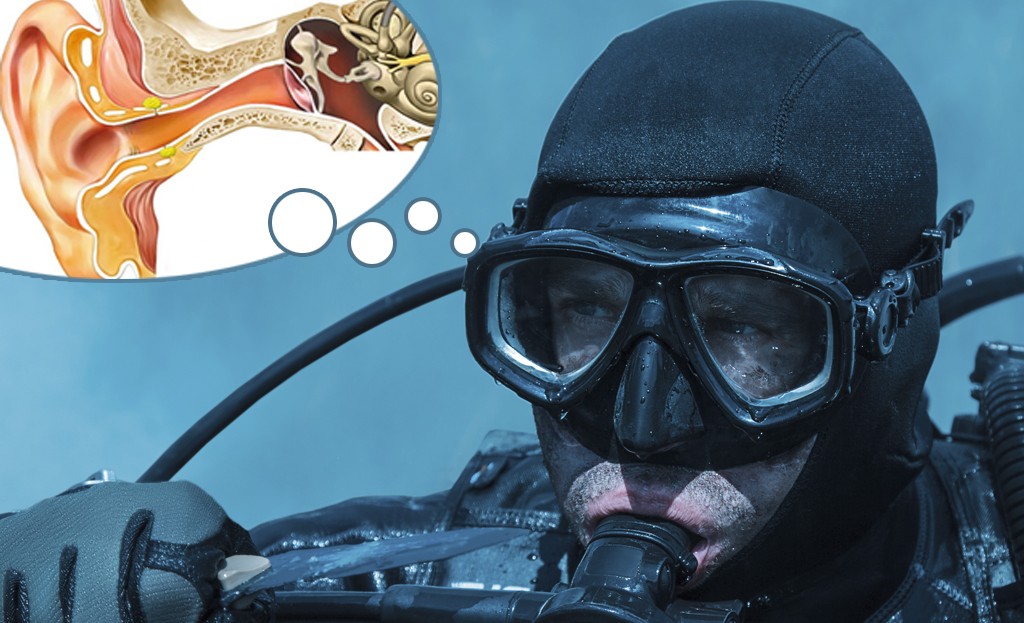
My ears hurt when diving
Whether scuba diving or free diving,
carrying an equalization maneuver to balance the atmospheric pressure and the internal pressure of the air lodged in the Eustachian tube of the middle ear is essential in order to avoid earache when diving. Diving slowly, in control of the situation will help these exercises come more naturally and spontaneously each time.
Diving without equalizing the pressure on the ear can cause middle ear barotrauma. To do this, the equalization maneuvers taught and practiced in diving courses are used, such as the Frenzel maneuver, by closing the mouth and nose to retract the glottis and thus equalizing the pressure, or the Valsalva maneuver, which consists of covering the mouth and exhaling through the nose.
Sometimes, climbing a mountain pass, traveling by plane or riding in an elevator causes this kind of pressure, just like when diving, especially in the first few meters.
Pressure increases twofold every ten meters of depth, both the pressure of the air at the surface and the pressure of the water, which combined make up the absolute pressure. Therefore, the first meters require being more cautious and performing the equalization maneuvers. If you feel pain due to the lack of equalization, ascend a little to balance pressures more easily.
It is also advisable to rise your nose before diving so that the ducts are clear of excess mucus, which will facilitate equalization. There are also masks with dry valves around the ears that help to reduce the impact of the water and facilitate equalization by isolating the ear canal for those who suffer from external and internal otitis, perforated eardrums or equalization problems.
In case of continuous earache, we always recommend that you visit an ear, nose and throat Underwater Medicine clinic.
 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences